Car-T cell therapy
CAR T – cell therapy is a type of treatment in which a patient’s T cells (white blood cells, vital components of the immune system) are modified in the laboratory to target and attack the cancer cells.
Initially, T cells are extracted from the patient’s blood and re-engineered in the laboratory to produce proteins on their surface called chimeric antigen receptors, or CARs.
Following the modification, a large number of the CAR T cells are grown in the laboratory and then administered to the patient through infusion.
CAR T cell therapies are personalized for each patient.
CAR T – cell therapy exhibits high effectiveness in combating certain types of hard-to-treat cancer like leukemia and lymphoma andis being studied for its potential application in treating various other cancer types.
However, it can also sometimes cause serious side effects like cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and nervous system problems.
Procedure
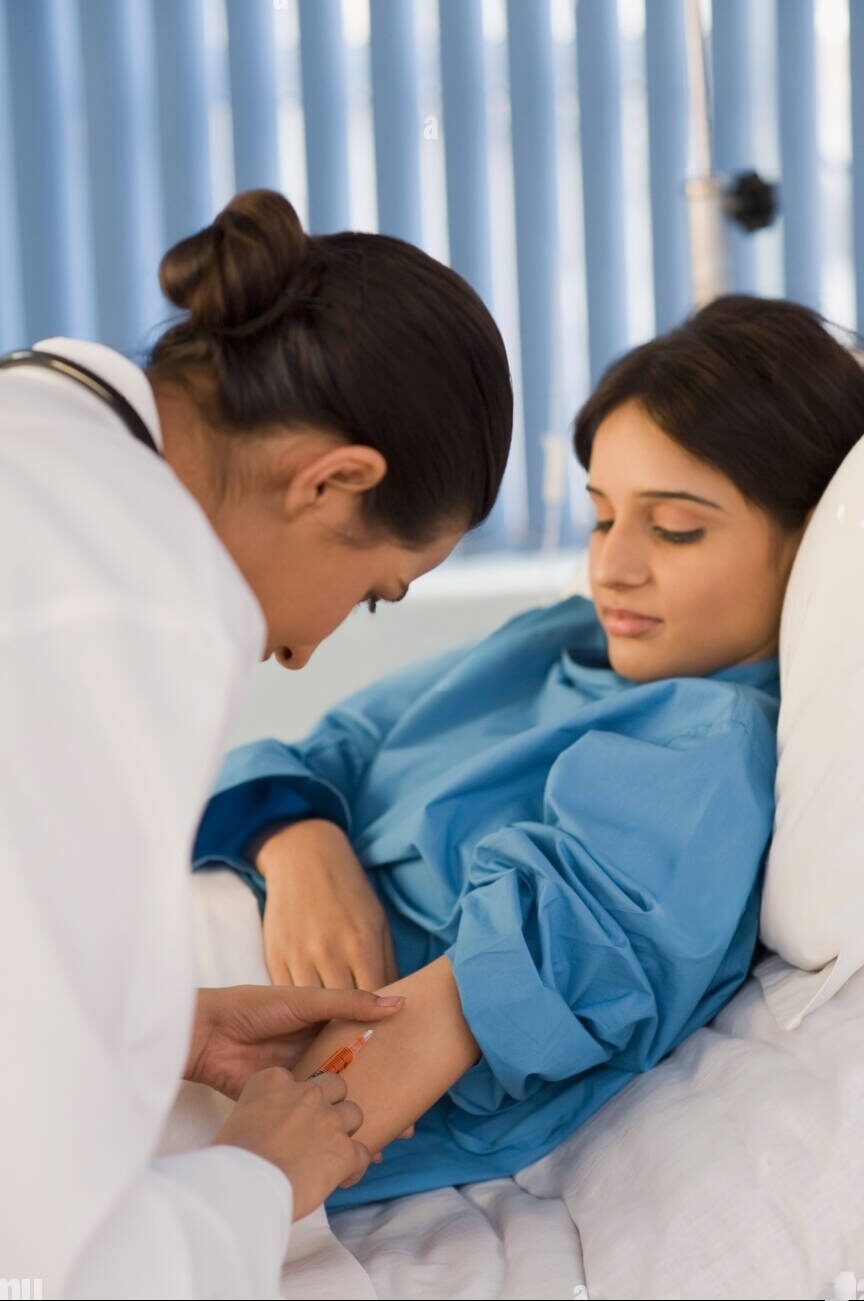
T Cells Collection
: Blood is extracted from a vein in the patient's arm. The blood flows through a tube into an apheresis machine (a device that processes whole blood to obtain one or more blood components). The machine removes T cells from the blood. Subsequently, the remaining blood components are returned to the patient’s body through a separate tube. The whole process is called Leukapheresis
CAR-T cells Manufacture
In the lab, the T cells are engineered by adding a manufactured CAR. This process converts them into CAR T cells. These cells are then cultured and multiplied within the laboratory setting.
CAR-T Therapy Administration
Once enough CAR T cells have been made, they will be infused into the patient. A few days before the CAR-T cell infusion, the patient might be given chemotherapy to help lower the number of other immune cells. This facilitates the activation of CAR T cells to fight the cancer. This chemotherapy is usually not very strong because CAR T cells work best when there are still some cancer cells to attack. Once the CAR T cells start binding with cancer cells, they start to increase in number, enabling them to effectively target and eliminate additional
Indications
The FDA has approved CAR-T therapy for the treatment of blood cancers such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), multiple myeloma(MM), and mantle cell lymphoma. The therapy benefits patients with relapsed or refractory hematological malignancies andsolid tumors
Advantages
CAR-T cell therapy offers the benefit of a relatively shorter duration for the completion of treatment. It surpasses traditional cancer treatments in achieving long-term remission with a better quality of life for patients. Compared to stem cell transplants, which require aggressive chemotherapy, CAR-T cell therapy typically leads to a faster recovery for the majority of patients. Unlike Tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and T cell receptors (TCRs), which are dependent on Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) expression of target cells for antigen recognition, CAR-T cells recognize the specific antigens, independent of antigen processing by the target cells and MHC restrictions, thus, allowing for effective killing of tumor cells.